Introduction to Turmeric
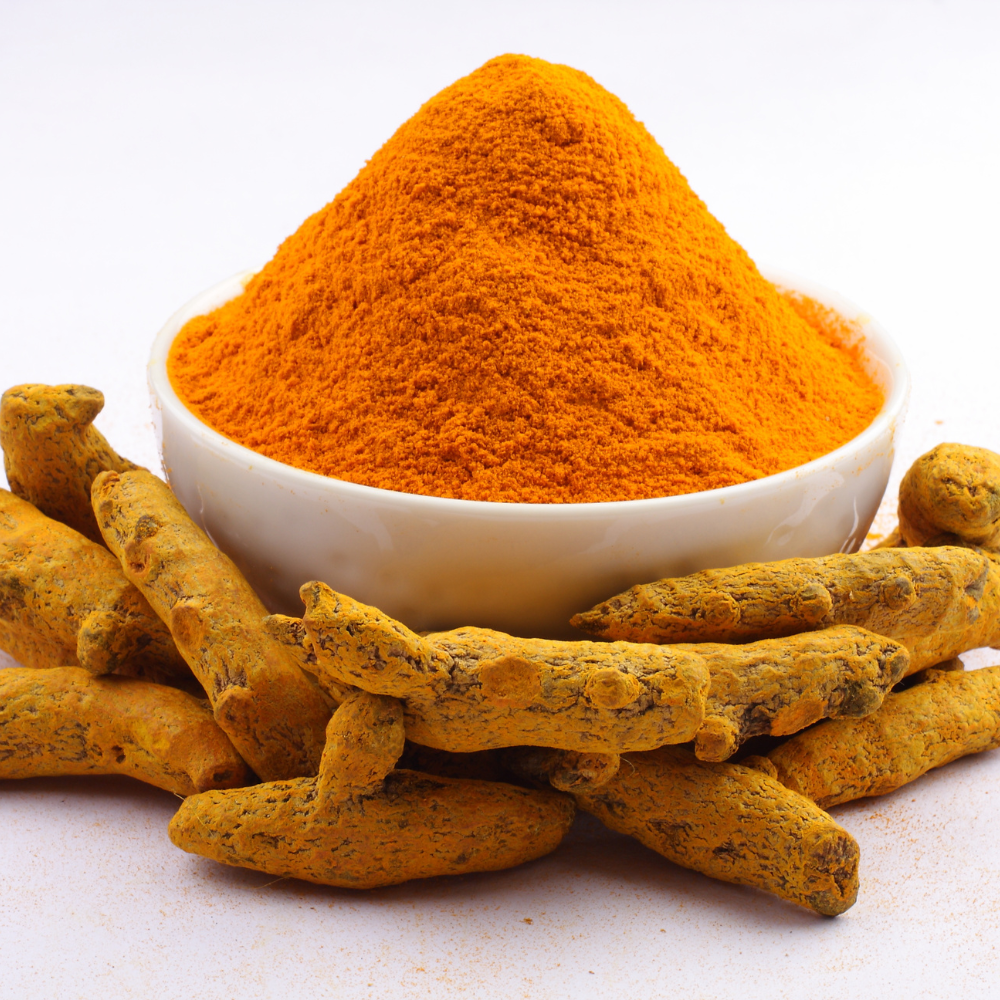
Turmeric, scientifically known as Curcuma longa, is a flowering plant belonging to the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It is primarily cultivated in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. The most notable aspect of turmeric is its rhizomes, which are underground stems that resemble ginger roots. These rhizomes are harvested, dried, and ground to produce the vibrant yellow powder known as turmeric.
Chemical Composition of Turmeric
Chemically, turmeric contains a variety of compounds, with the most significant being curcuminoids. The primary curcuminoid found in turmeric is curcumin, which is responsible for many of its health benefits and therapeutic properties. Curcuminoids are polyphenolic compounds with potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Other Compounds in Turmeric
Apart from curcuminoids, turmeric also contains volatile oils, such as turmerone, atlantone, and zingiberene, which contribute to its aroma and flavor. These volatile oils are responsible for the distinctive fragrance of turmeric. Additionally, turmeric contains other bioactive compounds like turmerin, sugars, proteins, and resins. These compounds collectively contribute to the diverse array of health benefits associated with turmeric consumption.

Health Benefits of Curcumin
Curcumin has been extensively researched for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anticancer, and neuroprotective properties. It scavenges free radicals, reduces inflammation by inhibiting various inflammatory pathways, and exhibits antimicrobial activity against bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Furthermore, curcumin has shown promise in preventing and treating various chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer.
Bioavailability Challenges
Despite its numerous health benefits, curcumin has low bioavailability, meaning that it is poorly absorbed by the body when consumed orally. To overcome this limitation, researchers have developed various formulations and delivery systems to enhance curcumin’s absorption and efficacy.
Conclusion
In summary, turmeric is a versatile spice with a complex chemical composition, primarily characterized by its curcumin content. Its rich array of bioactive compounds contributes to its therapeutic properties and makes it a valuable ingredient in traditional medicine and modern healthcare.

Note: While turmeric is generally safe for most people when consumed in moderation as a spice or dietary supplement, certain individuals should exercise caution or avoid it altogether. People who are allergic to turmeric or its components should avoid its consumption. Additionally, individuals with gallbladder problems, kidney stones, or those taking blood-thinning medications should consult a healthcare professional before using turmeric supplements, as it may interact with certain medications or exacerbate existing conditions. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should also consult their healthcare provider before using turmeric supplements. As with any dietary supplement, it’s essential to use turmeric responsibly and seek medical advice if you have any concerns or underlying health conditions.
Read More: Ready to dive deeper into the world of natural remedies? Check out our latest article – Turmeric – Its Nutritional Value